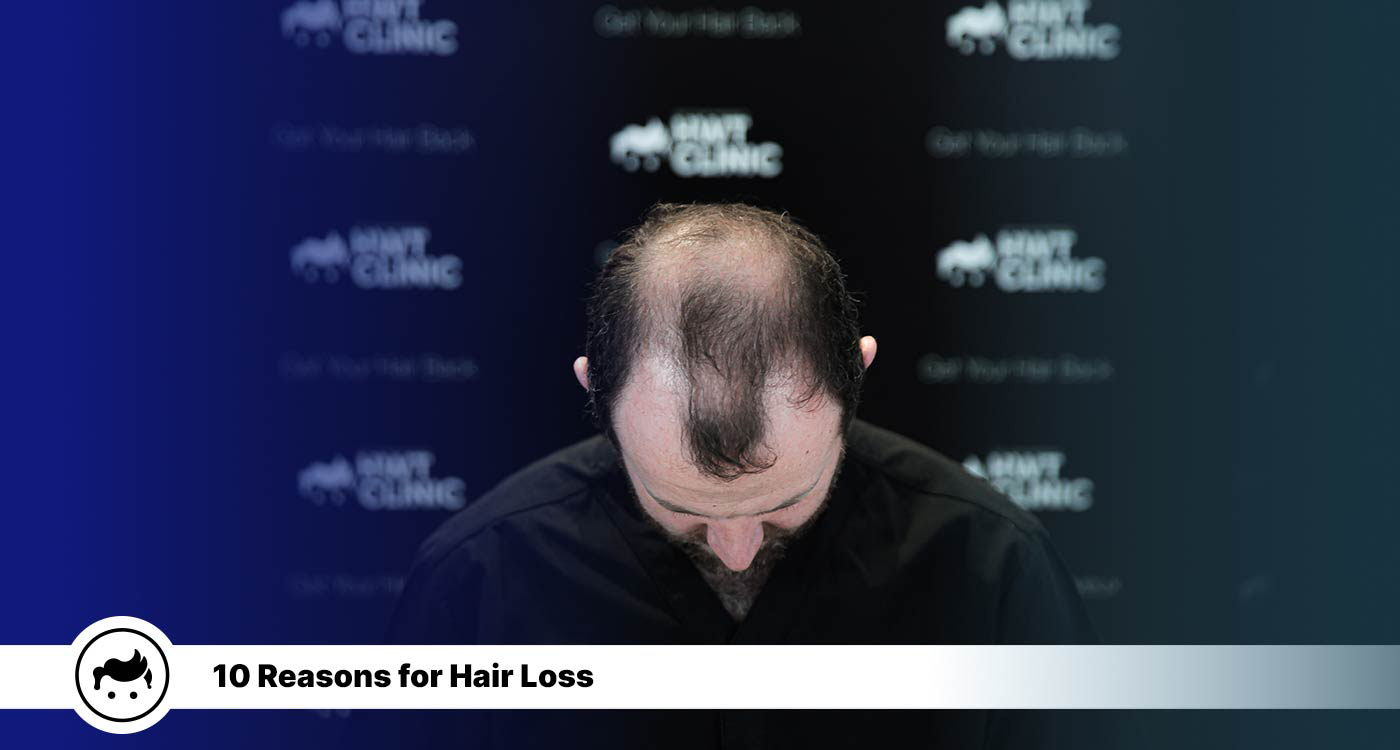
Hair loss, or alopecia, is defined by hair loss from the scalp and other body areas. It affects both sexes and has several probable causes, including genetics, hormonal fluctuations, sickness, and drug use. Androgenetic alopecia, alopecia areata, traction alopecia, anagen effluvium, and scarring alopecia are a few of the most common reasons for hair loss. Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common hair loss, described by a shrinking hairline and thinning at the crown in men and a gradual thinning of hair across the scalp in women. Its development is influenced by both genetics and hormones. Moreover, transitions in the hair’s growth cycle lead to a condition known as telogen effluvium or hair loss. Stress, hormonal shifts, and certain medicines possibly all play a role in bringing it on. There are ten most typical reasons for hair loss: hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, stressful events, specific prescriptions, thyroid problems, autoimmune diseases, physical trauma, trichotillomania, nutrient deficiencies, and extreme hair care. Hair thinning, receding hairline, progressive hair fall volume, patches of baldness, excessive shedding of hair, the emergence of tiny and circular patches, clumps of hair falling out, itching, redness, and scaling in the scalp, and a visible scalp are all symptoms associated with hair loss. Eating correctly, decreasing stress, avoiding tight hairstyles and harsh chemicals, switching to soft hair products, and seeing a dermatologist are all effective strategies to keep your hair from falling out. Hair loss is able to be treated with either conventional medicine or complementary therapies. The use of particular vitamins and supplements has shown promise in reversing and preventing hair loss. Further, men are twice as likely as women to have hair loss. Transplanting hair from one area of the scalp to another effectively cure baldness. However, hair transplants only work for some. Consultation with a medical professional is required before committing to Turkey hair transplant surgery.
Table Of Content
A hormonal imbalance exists when there is a discrepancy in the hormone levels produced by the endocrine glands. It is able to result in signs, including an increase in body weight or weight loss, fatigue, mood lability, and alterations in the body’s metabolism. Hormonal imbalances are able to be triggered by a variety of aspects, such as genetics, diet, stress, and particular health concerns. Furthermore, an imbalance in hormone levels is one of the causes of hair loss. One of the most common types of hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances is androgenetic alopecia, also called male or female pattern baldness. It is hair loss triggered by genetics and hormones, particularly an excess of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the body. DHT is a byproduct of testosterone that are able to lessen hair follicles, making it more challenging for hair to grow. Another typical mechanism by which hormonal imbalances bring hair loss is through changes in thyroid hormone levels. It is able to cause dramatic hair loss when the thyroid gland is overactive; it is able to cause the hair to thin and become brittle when it is underactive. Additionally, temporary hair loss might be brought on by hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause. Hair can enter the telogen phase of the hair development cycle because estrogen and progesterone levels drop during pregnancy and menopause. Some medications can alter hormone levels, which can therefore cause hair loss. It consists of drugs such as those used to treat depression, manage blood pressure, and prevent pregnancy
Pregnancy is the condition of being pregnant, where a woman bears a developing fetus inside the uterus. It typically lasts for about 40 weeks, or nine months, and is divided into three trimesters. Increased levels of estrogen in the body are able to prolong the growth phase of the hair development cycle. It means more hair remains on the head, and less fallout, leading to thicker, fuller hair. Meanwhile, the high levels of estrogen fall after giving birth, which is able to cause more significant numbers of hairs to enter the shedding phase of the hair growth cycle at the same time. It results in hair loss, which is called postpartum hair loss. Additionally, women experience hair loss during pregnancy as a side effect of certain medications, including prenatal vitamins and low-iron levels. It is common to lose some hair subsequently to giving birth since the hair that has fallen out during pregnancy is shed altogether. Postpartum hair loss usually starts around three to six months after giving birth and is able to last for several months.
A stressful event is any circumstance or experience that an individual perceives as complex or threatening to their welfare. It significantly influences an individual’s mental and physical health and results in various stress-related signs. Stressful circumstances are able to stimulate hair loss due to a process known as telogen effluvium. Stress is able to cause many hair follicles to penetrate the telogen phase of the hair growth cycle when a person is under a lot of pressure. It is easy to notice hair loss when a considerable number of hair follicles penetrate the telogen phase at once. Loss of hair due to stress often begins anywhere from a few weeks to three months after the stressful incident that caused the stress. It is also essential to remember that stress possibly induces other kinds of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia and alopecia areata.
Medication or medicine pertains to any substance used to treat, cure, or impede disease. They are able to be taken orally, applied topically, or directed through injections or other forms of administration. Medications cooperate with particular body molecules, called targets, which are able to be enzymes, proteins, or other molecules engaged in the disease process. Common medications are pain relievers, antibiotics, antidepressants, and hormones. Certain medications are able to cause hair loss as a side effect, which is called drug-induced hair loss or medication-induced hair loss. It takes place when the medication impacts the growth cycle of hair follicles, causing them to drop and stop generating hair. Some medicines are able to cause hair follicles to penetrate the telogen phase prematurely, leading to hair loss. The medication impacts the way that the body produces or processes certain chemicals or hormones that control the hair growth cycle. Hair loss is typically temporary, and the hair usually grows back once the individual stop taking medicines. Numerous pharmaceutical classifications are able to result in hair loss, including chemotherapy drugs, blood thinners, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, antidepressants, vitamin A derivatives, and hormone therapy.
The thyroid, a gland in the neck, is accountable for making hormones regulating the body’s metabolic rate. It is able to provoke issues that affect the body’s digestion and overall health when the thyroid gland generates outrageous or inadequate hormones. Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are the two primary issues that possibly arise with the thyroid. Hypothyroidism is an ailment that develops when the gland fails to generate sufficient hormones. The indications and signals include weariness, increased body weight, sensitivity to cold, and dry skin. Conversely, hyperthyroidism is when the gland makes abnormally enormous amounts of hormones. The symptoms include anxiousness, trembling, slimming, and a rapid heartbeat. Moreover, issues with the thyroid potentially lead to hair loss since the hormones generated by the gland are a factor in the growth and upkeep of hair. It drives thyroid ailments, a potential cause of hair loss. The body’s hormones become unbalanced when the thyroid gland is not operating as it used to, which impacts the cycle during which hair grows. The hair development cycle is slowed by hypothyroidism, which also causes the hair to become thinner and ultimately causes hair loss. Meanwhile, hyperthyroidism has been shown to induce hair loss due to an excess of thyroid hormones, which cause the hair development cycle to sped up, leading to hair loss.
Autoimmune diseases are situations wherein the body’s immune system falsely strikes and ruins healthy cells, organs, and tissues. The immune system recognizes and eliminates damaging trespassers involving bacteria and viruses. Conversely, autoimmune diseases incorrectly determine the body’s cells as foreign and launch an invasion against them. It leads to infection, damage, and destruction of particular organs and tissues. A few autoimmune diseases include lupus, type 1 diabetes, thyroiditis, and multiple sclerosis (MS). Additionally, autoimmune disorders induce hair loss since the immune system inaccurately strikes hair follicles, causing inflammation and hair follicle damage. It retards hair development, produces hair thinning, and induces hair loss. It impacts the scalp, like alopecia areata, resulting in patchy or total hair loss on the scalp. Moreover, lupus is an additional autoimmune disorder that is able to cause hair loss. It causes hair to be thin, fall out, become brittle, and readily break. Hair loss indicates an autoimmune attack on the thyroid gland in Hashimoto’s and Graves’ illnesses. Scleroderma, polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis are other autoimmune illnesses that induce hair loss.
Physical trauma is a bodily injury or wound caused by an external force, including a fall, a car crash, a gunshot, or a damaging attack. It is able to be caused by impacting the hair growth cycle. Scalp trauma makes the hair follicles penetrate the telogen phase prematurely, leading to hair loss by damaging the hair follicles. It is due to trauma that is able to break up the normal growth cycle of the hair follicles, causing them to stop generating new hair. The type of hair loss is well-known as telogen effluvium. It is essential to remember that hair loss caused by physical trauma is commonly a momentary side effect, and the hair typically grows back once the scalp has healed. However, hair growth is possible not to return if the hair follicles are severely destroyed.
Trichotillomania is a mental disorder distinguished by recurring and overpowering urges to draw out one’s hair, leading to hair loss and bald patches. It is a form of Boody-Focused Repetitive Behavior (BFRB). It occurs on any part of the body where hair is present. Someone with Trichotillomania pulls out hair in numerous ways, including plucking, twirling, and biting, which leads to hair loss. It results in bald patches or thinning hair in impacted areas. The hair loss generated by Trichotillomania is mild to severe and is able to scarring, infection, or other complications.
Nutrient Deficiencies happen when the body does not receive a sufficient level of the vitamins and minerals it needs to function appropriately. It occurs due to various factors, including poor diet, medical diseases, and certain medications. Some typical nutrient deficiencies are iron deficiency, vitamin D deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, folate deficiency, and vitamin C deficiency. Additionally, nutrients play a vital role in keeping good health, preventing disease, and preserving healthy hair. Hair loss is caused when the body does not get sufficient nutrients, including proteins, iron, and zinc. A lack of protein is able to cause hair to weaken and fall out, as hair is mainly made up of a protein called keratin. Moreover, iron is another essential nutrient for hair health, as it helps to bear oxygen to the hair follicles, which is needed for growth. Zinc helps to sustain healthy hair growth and repair. Zinc deficiency causes hair loss and changes in hair texture and color. It is vital to obtain a proper balance of nutrients to keep overall health and avoid hair loss. Eating a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps to ensure getting all the needed nutrients for healthy hair.
Extreme hair care is a term that pertains to various hair care practices intended to protect and repair hair that factors, including excessive styling, chemical treatments, or environmental stressors, have destroyed. It includes deep conditioning treatments, protein treatments, and protective hairstyles. Moreover, extreme hair care practices are able to cause hair loss if they are not used correctly or excessively aggressively. For instance, harsh chemical treatments, such as bleaches and relaxers, can destroy the hair shaft and follicles, making the hair more prone to breakage and loss. Additionally, using heat styling tools on a continual basis also causes damage to the hair and leads to hair loss over time. Furthermore, certain hair care practices, including tight braiding or cornrowing, cause hair loss if worn too tightly or for a long time. The tension from the braids puts stress on the hair follicles and makes them weak, then eventually stop producing new hair.
There are things to know about hair loss. The expected symptoms of hair loss are thinning of hair, shrinking hairline, gradual hair fall volume, patches of baldness, outrageous shedding of hair, the appearance of small and round patches, clumps of hair falling out, itching, redness, scaling in the scalp, and visible scalp. Furthermore, hair loss has many distinct causes, and each person is going to have a unique cause. The most frequent reasons are hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, stressful events, certain medications, thyroid problems, autoimmune diseases, physical trauma, trichotillomania, nutrient deficiencies, and extreme hair care.
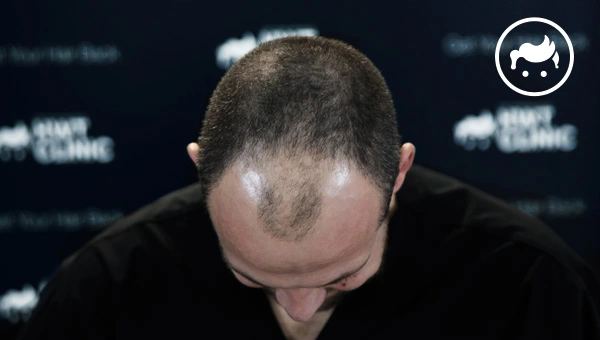
These hair loss symptoms are taken into account because they point to a decline in the quantity or density of hair on the scalp or other parts of the body. Numerous things interfere with the regular cycle of hair growth or harm hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It is vital to remember that shedding between 50 and 100 hairs every day is common and is a normal part of the hair growth cycle. However, it is essential to speak with a healthcare provider who is able to identify the root of the hair loss and suggest the best course of action if there are other changes in the hair or are losing a lot of hair.
Listed below are the six ways to prevent hair loss.
Listed below are the tips for having healthy hair.
Treatment options for hair loss are numerous and include medical and non-medical procedures. The underlying reason for the hair loss is going to determine the best course of action. Medical treatments for hair loss are medications, hormone replacement therapy (HRT), scalp micropigmentation, and Turkey hair transplant. Medications, including Minoxidil (Rogaine), Finasteride (Propecia), and Dutasteride (Avodart), slow down or stop hair loss and encourage the growth of new hair. Medications work by addressing the underlying causes of hair loss, such as hormonal imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, and certain medical conditions. However, they are not appropriate for everyone, and it takes several months before they fully manifest their effects. Moreover, Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is able to assist in addressing hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances, including those that appear during menopause or after pregnancy. HRT functions by substituting hormones that the body no longer produces, which assist in regulating the hair growth cycle and promoting healthy hair growth. It also replenishes the body’s levels of estrogen and progesterone to improve the condition of the hair and scalp. Additionally, a cosmetic procedure called scalp micropigmentation (SMP) addresses hair loss by delivering the impression of a full head of hair. SMP is a type of tattooing whereby microscopic spots of color are deposited on the scalp to mimic the appearance of short hair stubble. SMP is a successful therapeutic option for people with hair loss brought on by disorders like male or female pattern baldness, alopecia, or hair loss brought on by medical procedures like chemotherapy. Other medical treatments are Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT). PRP therapy is a non-surgical treatment that stimulates hair growth by using the patient’s blood plasma, which is high in growth factors, while low-level laser therapy (LLLT): LLLT is a non-invasive treatment that stimulates blood flow to hair follicles and promotes hair growth by using low-level laser light. Furthermore, Turkey hair transplant is a surgical procedure used to treat hair loss by transplanting hair follicles from a healthy part of the scalp to a bald or thinning area. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) are the two ways that are generally used to do the surgery.
On the other hand, non-medical treatments for hair loss are scalp massages, diet and nutrition, topical treatments, hairpieces and wigs, lifestyle changes, and concealers. Blood flow to hair follicles increases during a scalp massage. Increased blood flow gives oxygen and nutrients to hair follicles, strengthening and nourishing them. Scalp massage also stimulates hair follicles to develop new hair. It also loosens and eliminates oil, dandruff, and other debris that are able to block hair follicles and hinder hair growth. Additionally, diet and nutrition are crucial factors in hair health. A well-balanced diet high in vitamins and minerals promotes hair development and prevents hair loss. Protein, iron, vitamin D, vitamin C, and zinc are vital nutrients for hair health. Moreover, hairpieces and wigs conceal hair loss. They help people with hereditary, medical, or hair-thinning hair loss. Hair extensions are bits of natural or synthetic hair added to the hair. They complement your hair color and add volume and length. They are available in a variety of designs and colors and are composed of natural hair or synthetic fibers. Some wigs have adjustable straps to assist in holding the wig firmly in place. Furthermore, changes in lifestyle assist in encouraging hair development and preventing hair loss. Quitting smoking, decreasing stress, getting adequate sleep, avoiding tight hairstyles, avoiding heat styling, and avoiding harsh chemical treatments are some of the lifestyle modifications that assist in maintaining hair health. Lastly, concealers help disguise thinning hair. They are available in a variety of forms, including powders, sprays, and fibers, and possibly be customized to match your natural hair color. One of the most popular concealers is hair-building fibers. They are composed of keratin protein and are statically charged to cling to existing hair. They thicken hair and hide thinning hair. Hair thickening sprays thicken and volumize hair.
The best treatments for hair are medication, hair transplants, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and low-level laser therapy. The two things needed to pinpoint the cause and resolve the Hair loss: Diagnosis and treatment. A physical examination and a study of the patient’s medical history are usually used to determine the reason for hair loss. Healthcare experts do a scalp examination, a pull test, or a biopsy to determine the reason for hair loss. They also inquire about the patient’s food habits, medicines, and any other signs of hair loss. A healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or trichologist, is going to recommend treatments for hair loss after a proper diagnosis has been made.
A person has the possibility to encounter hair loss if they do not acquire enough of certain vitamins and minerals necessary for healthy hair. Vitamin A assists in preserving the scalp healthily and promotes new hair growth. Collagen is essential for the health and strength of hair and can only be produced with vitamin C. A lack of vitamin D has been linked to thinning hair because of its involvement in hair development and maintenance. The antioxidant properties of vitamin E make it helpful in preventing free radical damage to the hair. Biotin (B7), Niacin (B3), Vitamin B12, and Vitamin B6 are essential B vitamins for healthy hair. A lack of iron has been linked to thinning hair, as iron is essential for carrying oxygen to the hair follicles. Hair loss is possibly caused by a lack of zinc, which is essential for healthy hair development and maintenance. Protein is the primary structural component of hair; therefore, getting enough of it in the diet is crucial for a full head of healthy locks.
Nutrafol, Vitafusion Multivitamin Plus Beauty, and Nature’s Bounty Biotin are some of the best supplements for hair loss. Nutrafol is a dietary supplement that is marketed to promote healthy hair growth. It is full of vitamins, minerals, and natural compounds, including ashwagandha and saw palmetto. The doctor possibly suggests trying Nutrafol if suffering hair thinning or loss. The FDA has not authorized it as a medicine, and there is no concrete evidence that it promotes hair growth, but it does include all-natural substances with anecdotal reports of success. Each bottle of Nutrafol costs $88. Moreover, gummy vitamin Vitafusion Multivitamin Plus Beauty is promoted to support strong, healthy hair, skin, and nails. It contains a blend of vitamins, minerals, and other ingredients, such as biotin and collagen, known to have some benefits for hair, skin, and nail health. The gummy form of the supplement is easy to consume and is an alternative to traditional pill-form vitamin supplements. Vitafusion Multivitamin Plus Beauty Turkey hair transplant cost $11. Meanwhile, Nature’s Bounty Biotin is a dietary supplement that possesses biotin, a B-vitamin also known as vitamin H. Biotin is a B vitamin that plays a crucial role in energy production and is also beneficial for your hair, skin, and nails. A lack of biotin possibly results in hair loss and brittle nails. Thus, people with hair loss or brittle nails are often advised to take biotin supplements since a biotin deficit possibly results in these symptoms. Biotin from Nature’s Bounty comes in a variety of formats, including pills, gummies, and soft gels; it’s also often included in multivitamins. The price of Nature’s Bounty Biotin is $9 per bottle.
Yes, hair transplants can lessen hair loss. It covers hairless or thinning patches on the scalp and decreases hair loss. The approach is possibly advantageous as hair follicles are captured out of a scalp part where hair loss is not occurring. It implies that the hair implanted there is unaffected by the hereditary or hormonal elements inducing hair loss in the hairless or thinning area. Transplanting hair from a healthy and developing part of the scalp to a balding or thinning part is how a hair transplant operation works to make bald spots less conspicuous. It is not a durable remedy, even if Hair Transplant is possibly helpful for hair loss by reason of genetic factors like male or female baldness. The transplanted hair usually persists in growing and shedding, and hair loss is probable around the areas.
Yes, specific vitamins and minerals can help stop or slow hair loss. However, it is crucial to remember that many reasons possibly contribute to hair loss, and not all supplements are going to work for everyone. It is always a good idea to speak with a medical practitioner before beginning any new supplement regimen, mainly if there is a sign of losing hair. They are able to propose specific lab tests to see if a person is deficient in any particular nutrient causing hair loss and provide a customized treatment regimen.
No, men encounter hair loss more oftentimes than women do. Androgenetic alopecia is an inherited hormonal disorder that primarily concerns males. Androgenetic alopecia, frequently understood as female pattern baldness, is a genetical and hormonal condition influencing a far lower proportion of women than males. Males (70%) and females (40%) are more prone to permanent hair loss. Hair loss affects at least 85% of males by age 50, and 40% of females notice thinning hair by 40.




