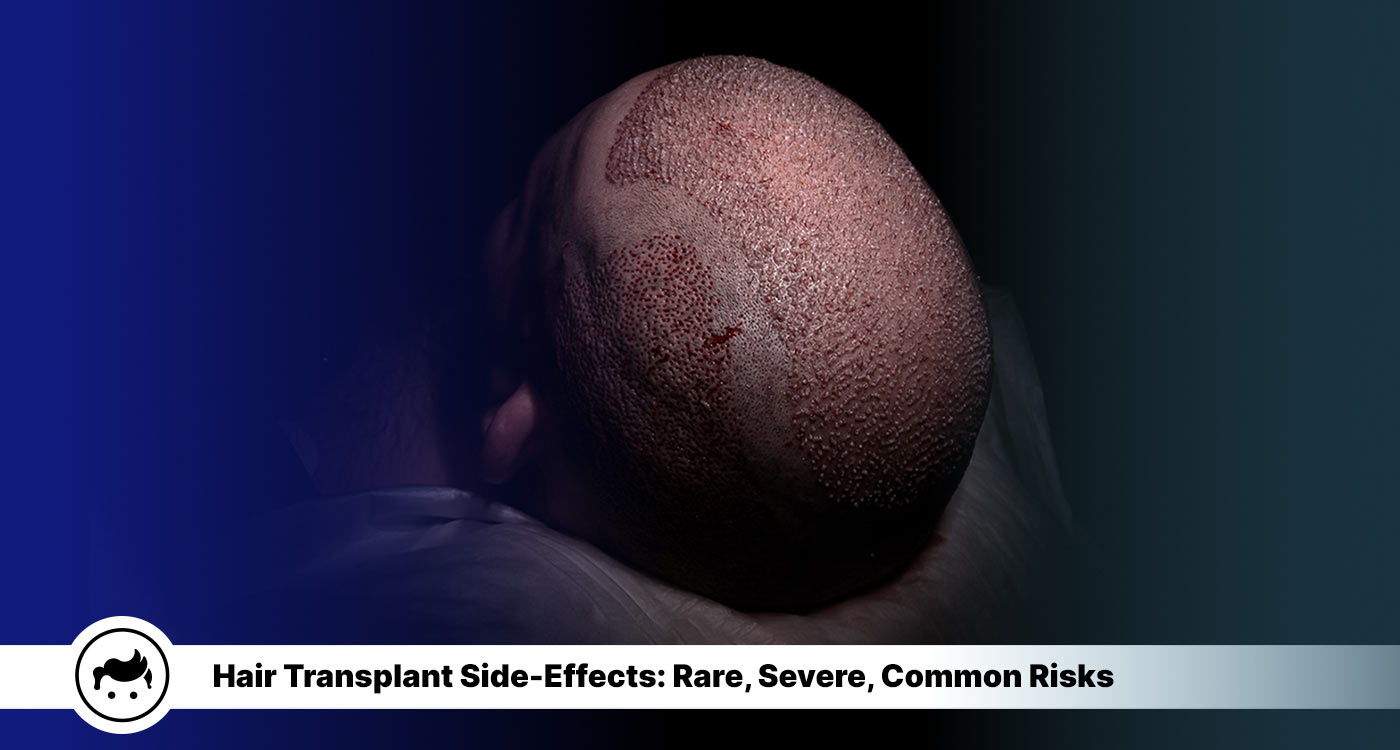
Transplanting hair from one part of the scalp to another is a typical operation in hair restoration surgery. The procedure is generally considered safe and effective for treating hair loss in males and females. It is important to know about the side effects so that an individual makes an informed decision about whether or not to undergo the procedure. Knowing the risks associated with this surgery helps to decide if it is right. Hair transplant refers to the larger context in which the procedure takes place. It includes the social, cultural, economic, and political factors that influence the decision to undergo hair transplant surgery, as well as the availability and accessibility of the procedure. It is important to understand the macro-context of hair transplant because it affects the patient’s decision-making process and the outcomes of the surgery. The social and cultural norms of a particular society influence the perceived attractiveness of different hairstyles and the pressure to conform to certain standards of appearance. Economic factors, such as the procedure’s turkey hair transplant cost and insurance coverage availability, play a role in the decision to undergo hair transplant surgery. Understanding the macro-context helps healthcare providers tailor their care to meet their patient’s specific needs and expectations and address potential barriers to care. It helps researchers and policymakers understand the factors influencing the demand for hair transplant surgery and the factors that impact its accessibility and availability. According to the National Library of Medicine, hair transplantation complications are rare due to the scalp’s strong blood supply, which allows for quick healing and low infection rates. However, some potential complications include oedema (occurring in 5% of cases), bleeding (occurring in 0.5% of cases), folliculitis, temporary numbness of the scalp, temporary shedding of native hairs at the donor or recipient site, epidermal cysts, ingrown hairs, and infection (affecting less than 1% of patients). Many patients wonder, “Do hair transplants hurt?” Typically, discomfort during the procedure is minimal due to local anesthesia, though some soreness and mild pain may be experienced afterward. Most complications are self-limited and are treated with warm compresses, shampooing, and antibiotics if necessary.
Listed below are the fifteen side-effects of Turkey hair transplant surgery.
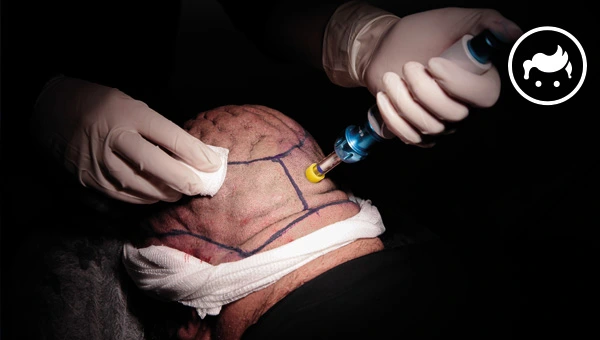
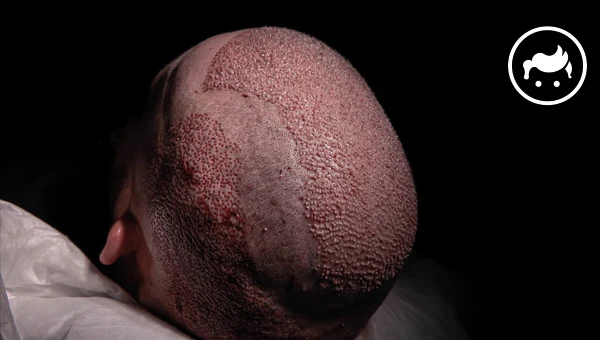
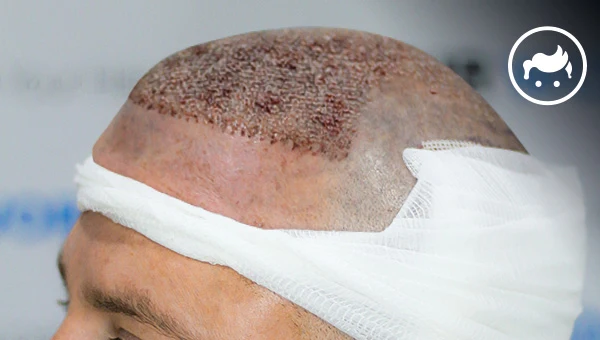
The most common side effects of a Turkey hair transplant procedure are swelling of the scalp, bruising, and pain. The side effects are typically mild and resolve independently within a few days to a week after the procedure. Other possible side effects of a hair transplant include bleeding, infection, and allergic reactions to the anesthesia or other medications used during the procedure. Understanding hair transplant risks is crucial before undergoing the procedure, including potential complications such as bleeding, scarring, and temporary shock loss.
Table Of Content
The bleeding scalp after a hair transplant is a common condition caused by the trauma of the procedure and the use of instruments. There are three types of bleeding scalp conditions: immediate bleeding, which occurs shortly after the procedure; delayed bleeding, which occurs a few days to a week after the procedure and is caused by the breakdown of blood clots; and continuous bleeding, which is caused by a damaged blood vessel. The severity of the bleeding depends on the type and location of the bleeding and is more likely to occur in people with certain risk factors. The FUT and FUE techniques potentially cause some scalp bleeding. Dr. Jerry Cooley is a specialist in this field.
Hair thinning, known as “shock loss,” is a temporary condition after a hair transplant. It is characterized by the shedding of both transplanted and non-transplanted hairs, leading to decreased hair density. There are two subtypes of hair thinning, telogen effluvium and androgenetic alopecia. Telogen effluvium is caused by physical or emotional stress, surgery, or certain medications and usually resolves on its own within a few months. Androgenetic alopecia is caused by inherited sensitivity to a hormone and occurs more frequently in patients predisposed to it. Hair thinning ranges from mild to severe and occurs in about 10-15% of hair transplant cases. The Norwood Scale, developed by Dr. O’Tar Norwood, is a widely used classification system for male pattern baldness that helps improve the accuracy and predictability of hair transplant procedures.
Itching is a normal part of the healing process after a hair transplant. It occurs as hair follicles repair and new hair begin to grow. The severity of itching varies from mild to severe and is more common in certain techniques like FUT and less common in techniques like FUE. Dr. Robert Bernstein, a renowned hair restoration surgeon and founder of Bernstein Medical, has made significant contributions to the field of hair transplantation and the development of techniques like FUE.
Infections on the scalp occur after a hair transplant procedure and range from mild to severe. Causes include poor hygiene, improper aftercare and contaminated instruments. Types of scalp infections include folliculitis, cellulitis and abscesses. The severity varies depending on the type and extent of the infection. Hair transplant infection is a potential risk following the procedure, but with proper post-operative care and antibiotic treatment, infections can often be prevented or managed effectively. Proper care and treatment resolve mild infections, while more severe infections require additional treatment such as antibiotics or surgical drainage. Proper aftercare and maintaining good hygiene help minimize the risk of scalp infections after a hair transplant. Dr. Norman Orentreich made significant contributions to the field, developing the concept of hair transplantation in the 1950s and conducting pioneering research on the use of hair transplantation to restore hair loss caused by male pattern baldness, which set the foundation for modern techniques.
Scarring after a hair transplant procedure refers to the formation of scar tissue at the site where hair follicles have been transplanted. Several types of scarring occur, including linear scarring, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation, and keloid scarring. The severity of scarring varies and depends on the transplant’s technique, the surgeon’s skill, and the individual’s healing process. The traditional strip method of hair transplantation (Follicular Unit Transplantation or FUT) sometimes results in more noticeable scarring due to the linear incision made, while the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) method, which involves the removal of individual hair follicles without a linear incision, resulting in less noticeable scarring. Dr. Robert Bernstein, a renowned hair restoration surgeon, has developed techniques to minimize scarring and improve the aesthetic outcome of hair transplant procedures.
Cysts are closed sacs that contain fluids, gases, or other substances and occur anywhere in the body. Three main types of cysts occur epidermoid, pilar, and sebaceous after hair transplantation surgery. They are considered a rare complication of the procedure, but the risk is higher for people with a history of cysts or certain underlying medical conditions. It is unclear which hair transplantation techniques increase the risk of developing a cyst. Dr. Bobby Limmer, a board-certified plastic surgeon, has researched and published on hair transplantation, including the risk of developing cysts.
Pain is a common side effect of hair transplantation procedures and ranges in intensity from mild to moderate. It is experienced in the head’s scalp, forehead, and back. Several types of pain are experienced after a hair transplant, including incisional pain caused by the incisions made during the procedure, suture-related pain from the sutures used to close the incisions, swelling, and itching. The severity of the pain varies based on the individual and the technique used, with larger graft techniques such as strip harvesting or FUT potentially causing more pain than techniques using smaller grafts like FUE. Dr. William Rassman is a renowned researcher in hair transplantation, particularly for his work on FUE procedures.
It is common for the forehead and eyelids to swell two to six days after hair transplant surgery. The swelling is caused by several factors, such as edema (fluid accumulation in the tissue), hematoma (collection of blood outside of a blood vessel), seroma (collection of clear, watery fluid), or infection. Swelling severity varies from person to person and is determined by the size of the transplant and the healing process of the individual. Swelling peaks on the second or third day after the surgery and resolves within a week or two typically. However, every person is different, and some experience more or less swelling than others. FUT (follicular unit transplantation) and FUE (follicular unit extraction) hair transplant techniques cause swelling after the procedure. Dr. Raymond Konior, a hair loss specialist based in Chicago, IL, notes that swelling is a common and temporary side effect of virtually any surgical procedure and is usually not a cause for concern in hair transplant patients.
It is common for hair transplant recipients to experience numbness after the procedure. Anaesthesia usually numbs the area being treated during surgery due to local anesthesia. The numbness usually disappears within a few days to a week after the procedure. Two types of numbness occur after a hair transplant: partial numbness, when only part of the treated area is numb, and complete numbness when the entire treated area is numb. The severity of numbness varies from person to person, ranging from a mild tingling sensation to a complete loss of sensation in the treated area. The amount of local anesthesia used during the procedure affects the severity of the numbness. Numbness after a hair transplant is common, especially after procedures that involve large amounts of local anesthesia, such as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplantation. Dr. Bernard Nusbaum, a board-certified dermatologist, and hair transplant surgeon, is a leading researcher in the field of hair transplantation and has published many articles on the subject and contributed to developing new techniques.
Hiccups are a common side effect after a hair transplant procedure caused by various factors such as eating quickly, consuming carbonated drinks, or feeling anxious or stressed. Two types of hiccups occur, acute and persistent, with varying severity and duration. Hiccups are more likely in people who have undergone larger hair transplant procedures or have underlying medical conditions that increase their risk of hiccups. The FUE and FUT techniques, which involve transplanting individual hair follicles or a strip of scalp, respectively, to an area of hair loss, cause hiccups after the procedure. Dr. Blair P. Grubb has made significant contributions to the study of hiccups through his research and publications.
Chest pain is an uncommon but possible side effect of hair transplantation, caused by swelling, inflammation, nerve damage, or infection. It is acute (sudden and severe but short-lived) or chronic (persistent and lasting for several days or weeks). The severity of the pain ranges from mild to severe. It is important to seek medical attention if chest pain is experienced after a hair transplant, as it indicates a more serious underlying condition. Chest pain is not a typical complication of hair transplant procedures but occurs in people with underlying health issues or who have had a particularly complex or extensive procedure. Techniques such as FUE, FUT, and scalp reduction potentially cause chest pain. Dr. William Rassman is a renowned expert in the field of hair transplantation who has contributed to the advancement of techniques such as FUE and FUT and has published research on the safety and effectiveness of hair transplant procedures.
Sexual dysfunction is not a common complication following hair transplant surgery. Temporary changes in sensitivity or function of the genital area occur due to swelling or irritation but typically resolve within a few weeks or months. There are four main categories of sexual dysfunction: desire disorders, arousal disorders, orgasm disorders, and pain disorders. Dr. Dhanraj Chavan has stated that hair transplant surgery does not cause sexual dysfunction, as it is a mechanical process that does not directly impact sexual function. It is worth noting that temporary sexual dysfunction is a side effect of finasteride, a medication used to treat hair loss, but it is not very common and is not caused by the procedure itself.
The swelling that occurs after surgery, including hair transplants, is normal. However, suppose someone experiences swelling in their hands, feet, or breasts after a hair transplant. In that case, they need to speak with their surgeon or a medical professional, as it is a sign of an underlying medical condition or a complication from the procedure. Possible causes of hand, foot, and breast swelling after a hair transplant include edema, allergic reactions, infections, blood clots, and lymphedema. It only occurs in the area where the procedure was performed and resolved within a week. No known hair transplant technique causes hand, foot, and breast swelling. It is important to seek medical attention if someone experiences unusual or concerning symptoms after a hair transplant to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Headaches are a common side effect of hair transplant procedures and are caused by surgical techniques. Different headaches occur after a hair transplant, including tension headaches, migraines, and cluster headaches. Tension headaches are the mildest form, while migraines and cluster headaches are more severe. The severity and frequency of headaches vary based on the individual and the surgical technique used. Some people experience a headache immediately after the procedure, while others develop one several days or weeks later. Surgical techniques such as strip excision and follicular unit extraction cause tension and swelling in the scalp, which contributes to developing a headache.
Dizziness is a common side effect after a hair transplantation procedure, caused by factors such as sedation or anesthesia, head position, dehydration, or low blood sugar. The severity varies, with some experiencing mild dizziness that goes away quickly and others experiencing more severe dizziness that persists for longer. It is important to discuss potential side effects with a qualified healthcare provider before undergoing the procedure. Dr. Walter P. Unger is a well-known hair transplant surgeon and researcher who has made significant contributions to the field and has published articles on the subject, including work on micrografts and mini grafts, which improve the naturalness and durability of results.
Hair transplants are a popular option for many people looking to improve the appearance of their hair, but there are some rare side effects to be aware of. It’s important to understand what happens and how to spot any problems before they become serious although these risks are relatively small. Listed below are the rare side effects of hair transplants.
The severe side effects of hair transplants are listed below.
The following are some of the typical issues that can happen after a hair transplant.
Here are some safety tips to help avoid any complications from a hair transplant.
Dr. Aman Dua, MBBS, MD, FISHRS wrote an article about the ten side effects of hair transplant surgery. Dr. Dua has 14 years of experience in Dermatology and Hair Transplant and is the Chief Dermatologist, Co-Founder, and Managing Director at AK Clinics. The article aims to educate patients about the common side effects of hair transplant surgery and how to recover from them. The National Library of Medicine has an article about hair transplantation that discusses different techniques, complications, risks, and other relevant information about the procedure.
Listed below are the changes in side effects of hair transplant according to hair transplant types.
Follicular Unit Transplant
Follicular Unit Extraction
Generally, FUE (follicular unit extraction) and FUT (follicular unit transplantation) procedures have similar side effects, including swelling, numbness, pain, scarring, and itching. Side effects are fairly common due to the surgical procedure and the body’s natural healing process. It is usually temporary and resolves independently within a few weeks or months.
FUE hair transplantation involves making incisions in the skin and manipulating tissue and carries a risk of side effects as with any surgical procedure. FUE hair transplant side effects may include temporary swelling, itching, and numbness in the donor and recipient areas, which usually subside within a few weeks post-procedure. The body’s natural response to surgery is swelling and inflammation at the incision sites, which lead to discomfort and other side effects. Anaesthesia and other medications used during the procedure contribute to side effects. Possible side effects of FUE hair transplantation include pain, which is usually managed with prescribed pain medication; swelling, which usually subsides within a week; bleeding at the donor and recipient sites, which is controlled with direct pressure; infection at the donor and recipient sites, which is minimized by following the doctor’s instructions for wound care and taking any prescribed antibiotics; scarring at the donor site due to the small incisions made to extract the hair follicles; numbness or tingling at the donor and recipient sites, which is usually temporary and resolves on its own within a few weeks; altered hair growth, which result in an uneven or unnatural appearance; and allergic reactions to the anesthesia or other medications used during the procedure. The risk and specific side effects of FUE hair transplantation vary widely among individuals and depend on factors such as overall health, the extent of the procedure, and the individual’s response to the surgery and medications. Discussing any concerns about side effects with a doctor before the procedure is important. Most people who undergo FUE hair transplantation tolerate the procedure well and experience minimal side effects.
A FUT hair transplant leads to various unappealing results, from unnatural-looking locks to bumps and scarring. There is pain, tenderness, bleeding, swelling, cysts or numbness. Reasons range from the direction of transplanted strands, their thickness or color, infection, nerve injury, scar formation or an immune reaction by the body. Ultimately, anyone considering FUT hair transplant treatment has to be aware that side effects vary in seriousness and likelihood depending on general health, how much hair has been lost and what techniques were used during the process. It is important to carefully follow all post-treatment advice and take any prescribed medications as instructed to reduce any risk of complications.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) hair transplantation is a medical procedure in which a person’s blood is drawn. The plasma is separated and injected into the scalp to stimulate hair growth. There are some potential side effects that people experience while PRP hair transplantation is generally considered safe. It includes dizziness, nausea, scalp pain, irritation during the healing process, scar tissue at the injection site, and injury to blood vessels and nerves. The side effects of PRP hair transplantation are related to the procedure itself or the medications used during the procedure. It is possible for anyone who undergoes PRP hair transplantation to experience side effects. Still, not everyone who undergoes the procedure experiences them, and many people do not have significant or long-lasting effects.
The Turkey hair transplant is a medical treatment that involves moving hair from one part of the body, called the donor site, to a bald or balding part of the body, known as the recipient site. The procedure is often used to treat male pattern baldness, a common form of hair loss that affects many men. Hair loss is a distressing problem for a significant portion of the population, including up to 85% of males and 40% of females, and it becomes more common with age for both sexes. There are two main methods of hair transplantation: follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE). A strip of skin with hair follicles is removed from the donor site in FUT, typically the back or sides of the head, and dissected into individual follicular units, which are small groups of one to four hairs. The units are then transplanted to the recipient site. Individual follicular units are directly removed from the donor site using a small punch tool and transplanted to the recipient site in FUE. FUT and FUE procedures are done with local anesthesia and take several hours to complete. It is normal for the hair to fall out and then regrow over the next several months after the transplant. The newly transplanted hair grows like natural hair. It is important to note that hair transplants are not suitable for everyone, and a qualified healthcare professional is consulted to determine if the procedure is appropriate. 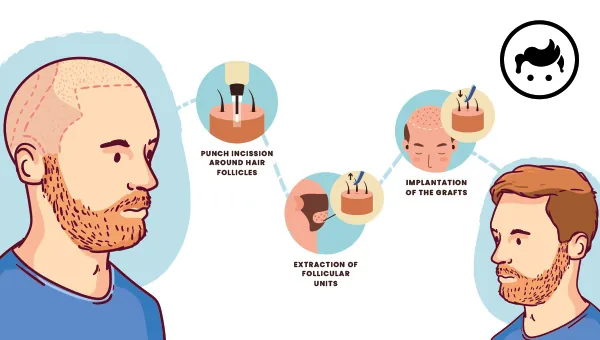
Hair transplant success rates are generally high, with 90-95% of grafted hair remaining in good condition. Patient satisfaction is often used to measure the success of a hair transplant. A study of patients who had received a combination of head and body/beard hair via FUE reported an average satisfaction rating of 8.3 out of 10 about three years after the procedure. It is important to note that it takes up to a year or more for the final results of a hair transplant to be visible, and some shedding of the transplanted hair is normal in the initial recovery period. A skilled surgeon needs to provide a full head of hair that lasts a lifetime, although the hair is still thin or grey due to natural aging.
No, hair transplant surgery is relatively painless, with most people not experiencing significant discomfort during or after the surgery. However, some individuals feel mild tightness or itching on the scalp. The area where the hair is transplanted is numbed with a local anesthetic before the procedure to minimize discomfort. Additionally, some people are given a sedative to help them relax during the surgery. The scalp is sore and tender for a few days after the procedure, but pain medication alleviates discomfort. Most people resume their normal activities within a few days of the surgery. However, it is important to follow the post-surgery instructions provided by the surgeon to ensure proper healing. It is important to speak with the surgeon beforehand if there are any concerns about pain during the surgery, to get more specific information and strategies for managing discomfort.
Hair transplant procedures sometimes have side effects, but the likelihood and severity of the side effects vary from person to person. Some people do not experience any side effects, while others have more noticeable side effects. The quality of the grafts and the technique used play a role in the appearance of side effects. Using lower-quality grafts or a less precise technique increases the risk of scarring or other unwanted side effects. Using high-quality grafts and a well-established technique help reduce the risk of side effects and improve the overall appearance of the transplanted hair. Talking to a qualified hair transplant specialist about a hair transplant procedure’s potential risks and benefits before undergoing any treatment is important.




